Summary: Augmented reality (AR) is one of the current technological trends that is spreading day by day. This technology allows to visualise the real-life environment with a digital augmentation overlay.
Currently, AR can be generated through applications on conventional devices such as smartphones, tablets, Hololens, etc. Little by little, this technology is looking for new application sectors to improve their workflows, especially in view of the arrival of 5G.
Google, Facebook and Amazon are some of the giants that use AR software to optimise their productivity. For example, Instagram or Snapchat create fun filters for their users.
Thus, augmented reality is defined as an altered form of reality in which computer-generated content is superimposed on the user’s real-world views, allowing digital assets to be added to their physical environment. AR must also meet three basic characteristics:
1. Combination of real and virtual world.
2. Real-time interaction.
3. Accurate 3D registration of real and virtual objects.
However, there are different types of ARs and their differences should be known, as each will be more suitable for a particular use, although they all share common features. Thus, the main differentiation will be between:
1. AR based on markers.
2. AR without markers:
- Location-based AR.
- Projection-based AR.
- Overlay AR.
- Contour-based AR.
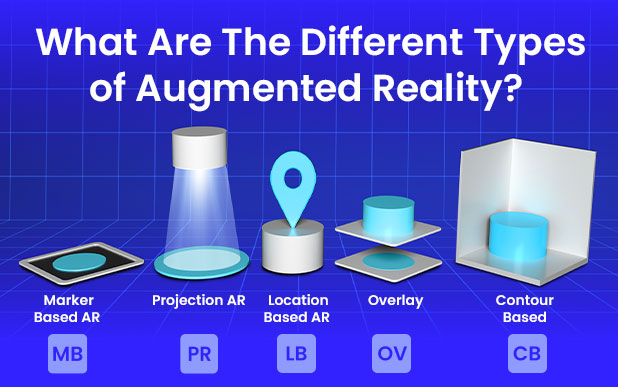
• MARKER BASED
also known as image recognition AR, requires a trigger photo or QR code to activate the experience.
• PROJECTION
uses a combination of projectors and vision sensors to display step by step interactive graphics onto any work surface.
• LOCATION BASED
primarily relies on GPS, accelerometer, digital compass, and other technologies to identify a phone's location and position with a high level of accuracy.